People do not give up their cultural identity at home, even if they may not be thinking about it. It impacts values, conduct, verbal exchange, and the way one of a kind individuals understand their position in the world. Culture as a concept is likely to be inherited, although it keeps on changing with time. It is not until their identity in their culture is threatened or not comprehended by others that many people start questioning their cultural identity. Knowing it assists in explaining experiences on a personal level and on one on a collective level.
What Cultural Identity Really Means

Cultural identity can be described as the common features that make people belong to a group. These traits may be language, traditions, beliefs, customs and social norms. It does not narrow down to nationality or ethnicity. Cultural identity is frequently a mixture of various influences affected by family, surroundings, and experience.
How Cultural Identity Is Formed
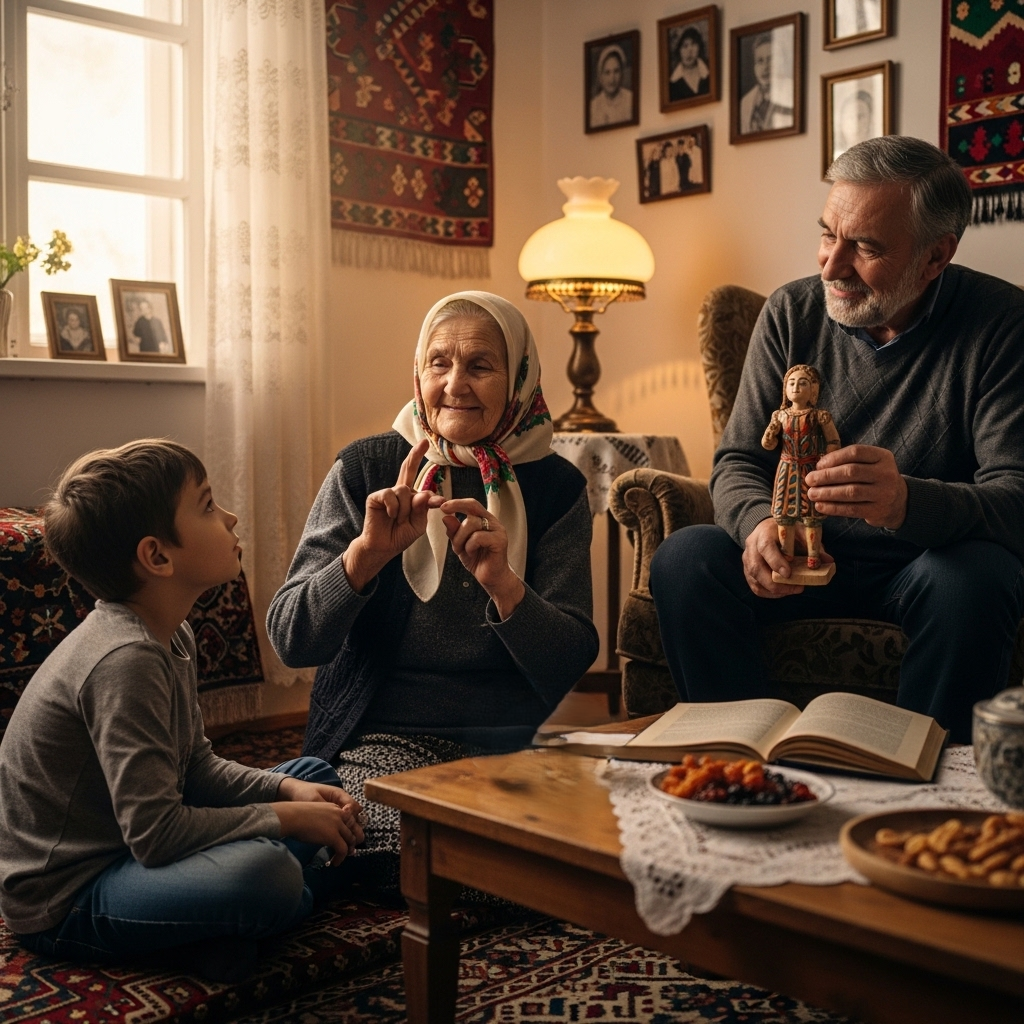

The socialization process develops cultural identity at a tender age. It is influenced by family, community, education and media. Exposure to other cultures may, over time enlighten or broaden identity. This is a continuous process as opposed to a fixed one.
Why Cultural Identity Creates Belonging
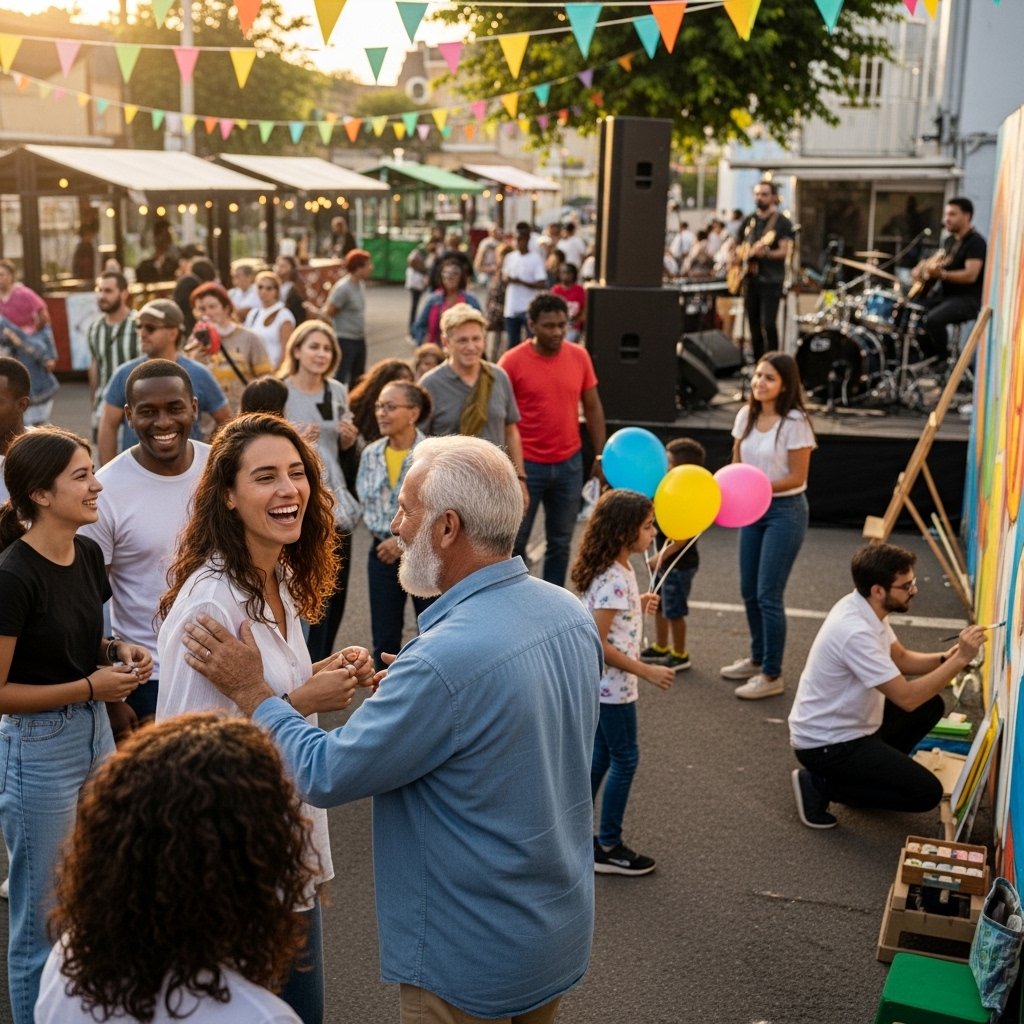

Man is a social animal; he wants affiliation. Cultural identification enables to provide inclusion and a not unusual information. It makes individuals feel a experience of belonging to a group. This community offers emotional nicely-being and social stability.
The Role of Cultural Identity in Self-Understanding

Being aware of cultural background is important in trying to explain personal values and reactions. It affects the manner in which individuals establish success, relationship and responsibility. Cultural awareness contributes to self-reflection. In the absence of it, identity may be disjointed or ambiguous.
Cultural Identity and Communication

Culture determines the way individuals show feelings, conflict, and behavior interpretation. This is normally misunderstood whilst cultural context isn’t taken into consideration. Cross-cultural cognizance enhances go-cultural communique. It lessens the diffusion and encourages compassion.
Preserving Traditions and History
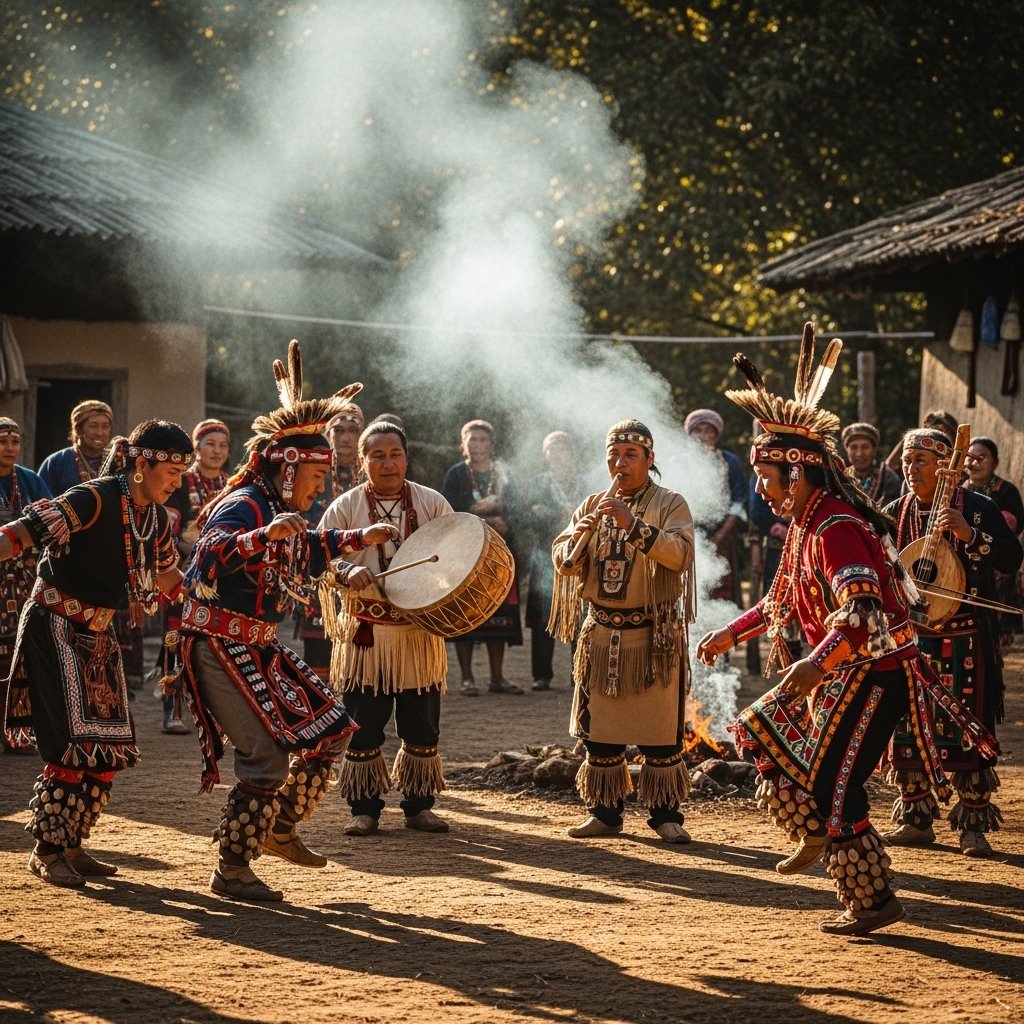

Cultural identity relates the current generations to the past. There are traditions, stories and rituals that have historical significance. Their continuity and collective recollection is preserved through their preservation. The aspect preservation enhances cultural resilience.
Cultural Identity in a Globalized World

Globalization is exposing individuals to a variety of lifestyles. Although this fosters exchange, it may also be a blurring of culture. Cultural identity assists in the battle of sustainedness amidst the flux. Balance permits adaptation to be erased.
How Cultural Identity Shapes Values

Moral codes of action are usually culturally oriented. Concepts of family, respect, and responsibility vary with culture. Knowledge of these origins averts judgment. It enables respectable co-existence.
The Impact on Social Cohesion

Good cultural identity creates united communities. Cooperation and trust are promoted through shared values. Social tension is reduced when cultural identities are observed. Togetherness is enhanced by inclusion.
Cultural Identity and Personal Confidence

Individuals knowing their cultural identity usually feel safe in accordance with the identity. Such trust decreases the level of seeking outside validation. The acceptance of ourselves enhances resiliency. Identity is clarity and helps one to be mentally and emotionally stable.
Why Cultural Identity Still Matters Today
Identity is becoming very imperative in a world that is becoming more interconnected. Cultural awareness promotes tolerance and not division. It assists societies in developing without losing meaning. It is built upon cultural identity rather than being a hindrance.
